DYNAMIC MODELING FOR THE LIFE CYCLE SUSTAINABILITY ASSESSMENT OF MICROALGAL BIOENERGY
The performance of PRODIGIO developments should be evaluated according to environmental economic and social criteria to ensure the improvement capacity of early-warning systems compared to systems without such technology.
A methodological framework based on life cycle thinking is used in PRODIGIO to account for these impacts influencing the sustainability of processes with a holistic approach, including from the raw materials extraction and transformation to the final biogas production and exploitation.
The level of sustainability of microalgal processes is highly dependent on variable parameters, such as microalgal productivity or composition. Thus, flexible Life Cycle Assessment models are needed to evaluate how variations of such operation parameters linked to the early-warning systems in PRODIGIO can affect the results on sustainability criteria analyzed through environmental impact categories or economic results.
To do so, ARMINES/MINES Paris is developing parameterized models, that is, mathematical models based on relationships between a set of input parameters (e.g. productivity, composition, temperature conditions etc) and the impacts of the process on the environment, on the economic costs, etc. These models allow not only the evaluation of fixed steady-state scenarios of algae cultivation, but also a dynamic analysis of the evolution of the algal culture and biogas production over time. To implement these models, we have used the python programming language, together with the related libraries Brightway2 (https://brightway.dev/), developed by Chris Mutel at the group for Ecological Systems Design of ETH Zürich, and lca_algebraic (https://github.com/oie-mines-paristech/lca_algebraic), developed by our own center, O.I.E., of ARMINES/MINES Paris.
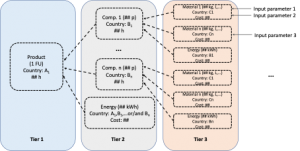
Figure: Simplified diagram representing the structure of parameterized models for Life Cycle Assessment
Dynamic modeling is essential to account for the effect of changes in the culture and, thus, to fully account for the potential of PRODIGIO developments to enhance the performance of systems.
Authors: Paula Pérez-López, Andriamahefasoa Rajaonison

